

Cochlear Implants Surgery
Home > Treatments > Cochlear Implants SurgeryCochlear Implants Surgery
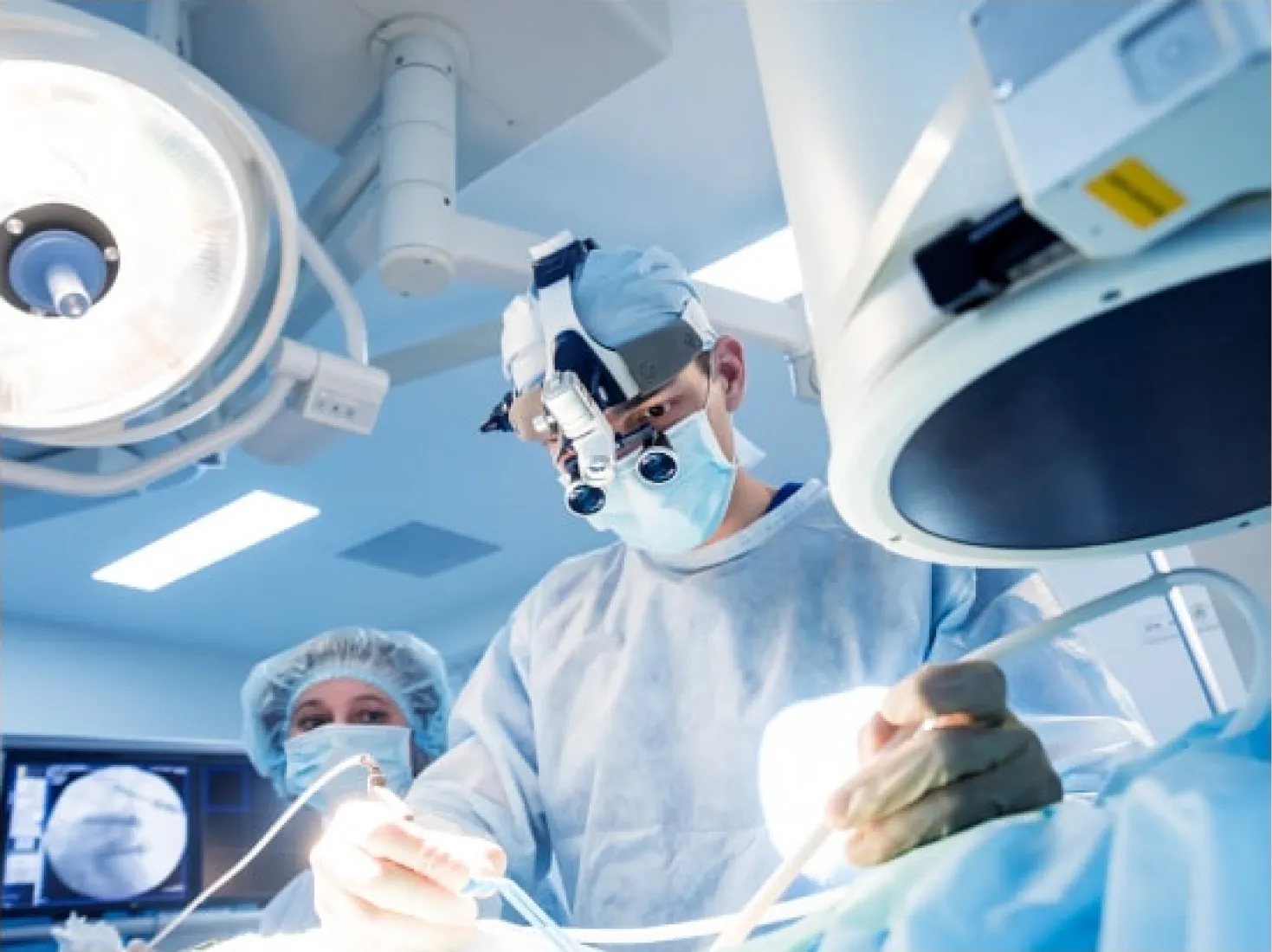
A cochlear implant is a surgically inserted electronic device designed to enhance hearing. It is particularly effective for individuals with severe hearing loss in one or both ears who struggle with communication despite using hearing aids.
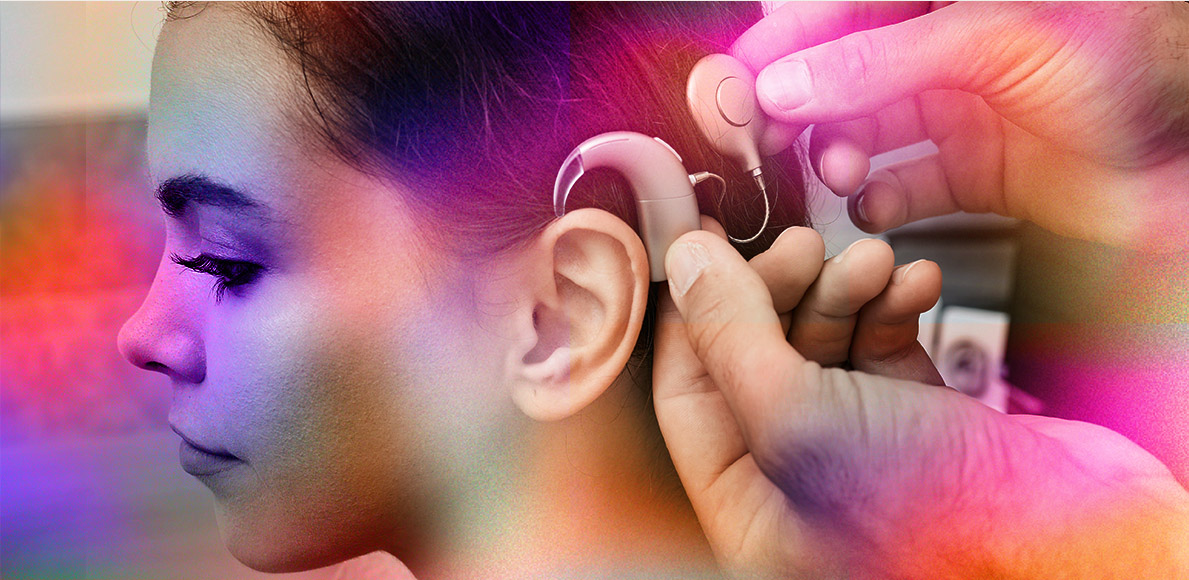
Cochlear implants are electronic devices designed to restore hearing for those who are deaf or have severe hearing loss. Unlike hearing aids, which amplify sound, cochlear implants work by bypassing the damaged hair cells in the inner ear and directly stimulating the auditory nerve, enabling the brain to interpret sound.
A cochlear implant bypasses damaged parts of the ear to send sound signals directly to the auditory nerve, unlike hearing aids, which simply amplify sound. When hearing aids are ineffective for severe hearing loss, cochlear implants can significantly improve hearing, enhancing communication and quality of life. These implants are suitable for individuals of all ages, from children as young as 6 to 12 months old to adults.
Cochlear implants can be used in one ear (unilateral) or both ears (bilateral). Adults often begin with one cochlear implant paired with a hearing aid, and if hearing loss worsens in the aided ear, they may eventually use cochlear implants in both ears. For children with severe bilateral hearing loss, cochlear implants are commonly placed in both ears simultaneously, particularly for infants and young children who are still developing their language skills.
Blogs

Established in 2007 with a commitment to excellence, KERF has grown to become a trusted name in ENT care, known for our expertise, compassion and innovation.
O P Timing : 9am - 1pm | 4pm - 6pm
Ⓒ 2024 KERF Hospital. All rights reserved | Designed by Codeface Technologies